LeakCanary Android 和 Java 内存泄露检测。 原文:https://www.liaohuqiu.net/cn/posts/leak-canary-read-me/
1
2
3
“A small leak will sink a great ship.” - Benjamin Franklin
千里之堤, 毁于蚁穴。 -- 《韩非子·喻老》
demo 一个非常简单的 LeakCanary demo: https://github.com/liaohuqiu/leakcanary-demo
开始使用 在 build.gradle 中加入引用,不同的编译使用不同的引用: 1
2
3
4
5
dependencies {
debugCompile 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android:1.5.1'
releaseCompile 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android-no-op:1.5.1'
testCompile 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android-no-op:1.5.1'
}
在 Application 中: 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class ExampleApplication extends Application {
@Override public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
if (LeakCanary.isInAnalyzerProcess(this)) {
// This process is dedicated to LeakCanary for heap analysis.
// You should not init your app in this process.
return;
}
LeakCanary.install(this);
// Normal app init code...
}
}
这样,就万事俱备了! 在 debug build 中,如果检测到某个 activity 有内存泄露,LeakCanary 就是自动地显示一个通知。
为什么需要使用 LeakCanary? 问得好,看这个文章: LeakCanary: 让内存泄露无所遁形
如何使用 使用 RefWatcher 监控那些本该被回收的对象。
1
2
3
4
RefWatcher refWatcher = {...};
// 监控
refWatcher.watch(schrodingerCat);
LeakCanary.install() 会返回一个预定义的 RefWatcher ,同时也会启用一个 ActivityRefWatcher ,用于自动监控调用 Activity.onDestroy() 之后泄露的 activity。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public class ExampleApplication extends Application {
public static RefWatcher getRefWatcher(Context context) {
ExampleApplication application = (ExampleApplication) context.getApplicationContext();
return application.refWatcher;
}
private RefWatcher refWatcher;
@Override public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
refWatcher = LeakCanary.install(this);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
使用 **RefWatcher** 监控 **Fragment**:
public abstract class BaseFragment extends Fragment {
@Override public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
RefWatcher refWatcher = ExampleApplication.getRefWatcher(getActivity());
refWatcher.watch(this);
}
}
工作机制
RefWatcher.watch() 创建一个 KeyedWeakReference 到要被监控的对象。
然后在后台线程检查引用是否被清除,如果没有,调用GC。
如果引用还是未被清除,把 heap 内存 dump 到 APP 对应的文件系统中的一个 .hprof 文件中。
在另外一个进程中的 HeapAnalyzerService 有一个 HeapAnalyzer 使用HAHA 解析这个文件。
得益于唯一的 reference key, HeapAnalyzer 找到 KeyedWeakReference,定位内存泄露。
HeapAnalyzer 计算 到 GC roots 的最短强引用路径,并确定是否是泄露。如果是的话,建立导致泄露的引用链。
引用链传递到 APP 进程中的 DisplayLeakService, 并以通知的形式展示出来。
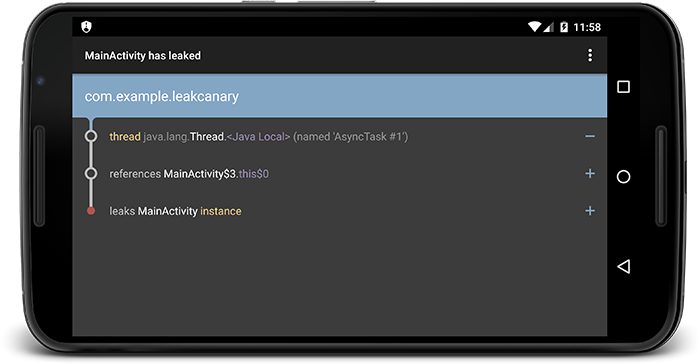
如何复制 leak trace? 在 Logcat 中,你可以看到类似这样的 leak trace:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
In com.example.leakcanary:1.0:1 com.example.leakcanary.MainActivity has leaked:
* GC ROOT thread java.lang.Thread.<Java Local> (named 'AsyncTask #1')
* references com.example.leakcanary.MainActivity$3.this$0 (anonymous class extends android.os.AsyncTask)
* leaks com.example.leakcanary.MainActivity instance
* Reference Key: e71f3bf5-d786-4145-8539-584afaecad1d
* Device: Genymotion generic Google Nexus 6 - 5.1.0 - API 22 - 1440x2560 vbox86p
* Android Version: 5.1 API: 22
* Durations: watch=5086ms, gc=110ms, heap dump=435ms, analysis=2086ms
你甚至可以通过分享按钮把这些东西分享出去。
SDK 导致的内存泄露 随着时间的推移,很多SDK 和厂商 ROM 中的内存泄露问题已经被尽快修复了。但是,当这样的问题发生时,一般的开发者能做的事情很有限。
LeakCanary 有一个已知问题的忽略列表,AndroidExcludedRefs.java,如果你发现了一个新的问题,请提一个 issue 并附上 leak trace, reference key, 机器型号和 SDK 版本。如果可以附带上 dump 文件的 链接那就再好不过了。
对于最新发布的 Android,这点尤其重要。你有机会在帮助在早期发现新的内存泄露,这对整个 Android 社区都有极大的益处。
开发版本的 Snapshots 包在这里: Sonatype’s snapshots repository。
leak trace 之外 有时,leak trace 不够,你需要通过 MAT 或者 YourKit 深挖 dump 文件。
通过以下方法,你能找到问题所在:
查找所有的 com.squareup.leakcanary.KeyedWeakReference 实例。
检查 key 字段
Find the KeyedWeakReference that has a key field equal to the reference key
找到 key 和 和 logcat 输出的 key 值一样的 KeyedWeakReference。
referent 字段对应的就是泄露的对象。
剩下的,就是动手修复了。最好是检查到 GC root 的最短强引用路径开始。
自定义 UI 样式 DisplayLeakActivity 有一个默认的图标和标签,你只要在你自己的 APP 资源中,替换以下资源就可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
res/
drawable-hdpi/
__leak_canary_icon.png
drawable-mdpi/
__leak_canary_icon.png
drawable-xhdpi/
__leak_canary_icon.png
drawable-xxhdpi/
__leak_canary_icon.png
drawable-xxxhdpi/
__leak_canary_icon.png
1
2
3
4
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="__leak_canary_display_activity_label">MyLeaks</string>
</resources>
保存 leak trace DisplayLeakActivity saves up to 7 heap dumps & leak traces in the app directory. You can change that number by providing R.integer.__leak_canary_max_stored_leaks in your app:
在 APP 的目录中,DisplayLeakActivity 保存了 7 个 dump 文件和 leak trace。你可以在你的 APP 中,定义 R.integer.__leak_canary_max_stored_leaks 来覆盖类库的默认值。
1
2
3
4
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<integer name="__leak_canary_max_stored_leaks">20</integer>
</resources>
上传 leak trace 到服务器 你可以改变处理完成的默认行为,将 leak trace 和 heap dump 上传到你的服务器以便统计分析。
创建一个 LeakUploadService, 最简单的就是继承 DisplayLeakService :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class LeakUploadService extends DisplayLeakService {
@Override
protected void afterDefaultHandling(HeapDump heapDump, AnalysisResult result, String leakInfo) {
if (!result.leakFound || result.excludedLeak) {
return;
}
myServer.uploadLeakBlocking(heapDump.heapDumpFile, leakInfo);
}
}
请确认 release 版本 使用 RefWatcher.DISABLED:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public class ExampleApplication extends Application {
public static RefWatcher getRefWatcher(Context context) {
ExampleApplication application = (ExampleApplication) context.getApplicationContext();
return application.refWatcher;
}
private RefWatcher refWatcher;
@Override public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
refWatcher = installLeakCanary();
}
protected RefWatcher installLeakCanary() {
return RefWatcher.DISABLED;
}
}
自定义 RefWatcher:
1
2
3
4
5
public class DebugExampleApplication extends ExampleApplication {
protected RefWatcher installLeakCanary() {
return LeakCanary.install(app, LeakUploadService.class);
}
}
别忘了注册 service:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
>
<application android:name="com.example.DebugExampleApplication">
<service android:name="com.example.LeakUploadService" />
</application>
</manifest>